A Guide to App Development with Python
It usually starts with a simple idea. A spark. But turning that spark into a functional application people can actually use feels like a huge leap, especially if you know Python mostly for its clean syntax in scripting or data science. You start to wonder, "Can my favorite language really build a full blown app?"
The good news? The answer is a resounding yes. App development with Python is not only possible but increasingly popular, thanks to its powerful frameworks and a community that has your back.
Why Build Your Next App with Python
Let us be honest, the path from a simple script to a production grade application can seem daunting. I remember feeling that mix of excitement and doubt, wondering if the language I loved for its simplicity could really handle the heavy lifting of a real world app. I got stuck on this for a while, wondering if I was making the right choice, or if I should be learning something else entirely.
That feeling is common, but the landscape has shifted dramatically. Python has broken out of its traditional boxes. It is no longer just the go to for data scientists and automation engineers; it has seen a major resurgence in web and application development, becoming a first class citizen for building robust, scalable systems.
The Numbers Tell the Story
Recent trends back this up. Python's usage in web development has been climbing steadily, with adoption projected to grow from 42% in 2023 to 46% by 2025. This growth is supercharged by modern frameworks like FastAPI, which saw its own adoption jump from 29% to 38% in the same timeframe.
The language's gentle learning curve and widespread appeal are key drivers, as detailed in surveys of over 30,000 developers. You can dig into the data yourself to see just how the community is evolving.
The infographic below really puts Python's advantages into perspective; developer productivity, library support, and web app growth all stand out.
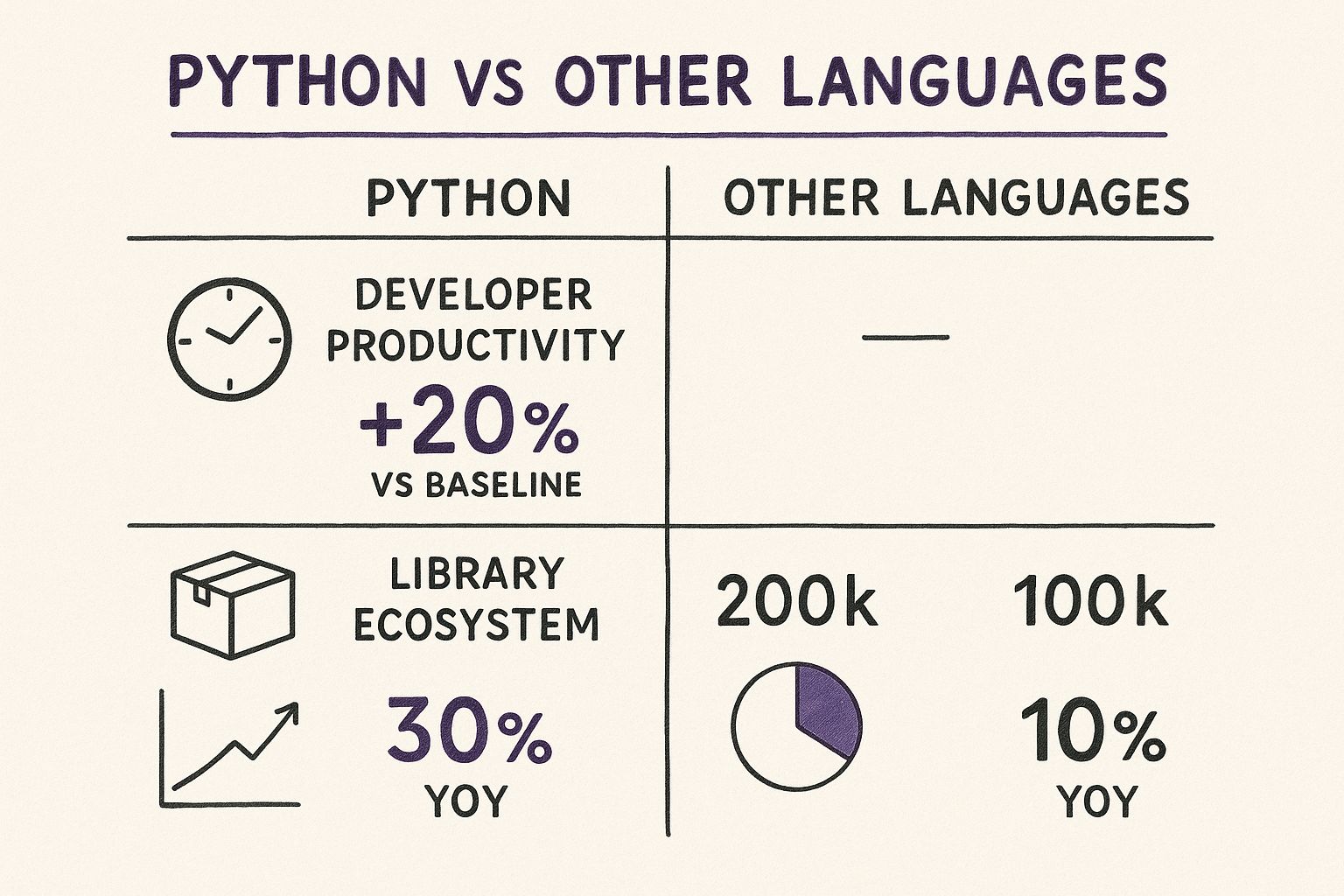
As you can see, Python offers a clear edge in getting things done faster and tapping into a massive ecosystem of pre built tools.
More Than Just Code
So, why are so many developers flocking to Python? It really boils down to a few core strengths that make the entire development process more humane and effective.
- Readability and Simplicity: Python's syntax is famously clean and reads almost like plain English. This means less time deciphering complex code and more time building features. Simple as that.
- Vast Library Ecosystem: The Python Package Index (PyPI) is a treasure trove of over 200,000 packages. Need to work with APIs, databases, or machine learning? I can almost guarantee there is a library for that.
- A Seriously Strong Community: When you inevitably get stuck on a bug at 2 AM (we have all been there), a massive, active community is ready to help through forums, documentation, and countless tutorials.
Choosing Python is not just a technical decision; it is a strategic one. It sets you up with a tool that prioritizes clarity, speed, and community support. In the next sections, we will move from this "why" to the practical "how," starting with the crucial choice of a framework.
Choosing Your Python Framework
Alright, let us talk about the first big decision you will make, the one that can send you down a rabbit hole of blog posts and forum debates for days: picking your web framework.

I have been there. Staring at my screen, stuck in analysis paralysis, wondering if I should go with the established, batteries included power of Django, the minimalist flexibility of Flask, or the new, high performance contender, FastAPI.
It is a classic developer dilemma. You feel like the fate of your entire project rests on this single choice. But here is the truth: there is no single "best" framework. It is about finding the right tool for the job you need to do and, just as importantly, the tool that clicks with your personal style.
Django: The All In One Powerhouse
Think of Django as the ultimate toolkit for building a house. It comes with everything you need right out of the box, from the foundation to the plumbing. This "batteries included" philosophy is its greatest strength and what makes it so productive.
You get a powerful Object Relational Mapper (ORM) for database interactions, a built in admin panel that is a massive time saver, and robust security features baked right in. I once built a prototype for a client with a complex user management system, and Django's built in authentication and admin saved me what felt like weeks of work.
- Best for: Content heavy sites like blogs or ecommerce stores, projects with complex user models, and teams that want a standardized, opinionated structure.
- Tradeoff: Django can feel a bit rigid. Its opinionated nature means you do things the "Django way," which can have a steeper learning curve if you are used to more freedom.
If you are leaning toward this structured approach, diving into a proper setup is key. We have a complete walkthrough on starting a Django project without the headaches that can help you sidestep common initial hurdles.
Flask: The Minimalist's Dream
If Django is a full toolkit, Flask is a single, high quality hammer. It is lightweight, unopinionated, and gives you the absolute essentials to get started. You decide which nails, screws, and other tools you want to bring to the job.
This microframework approach gives you total control. You choose your ORM (like the excellent SQLAlchemy), your validation libraries, and every other component. This flexibility is amazing for smaller projects, microservices, or when you have a very specific, non standard requirement that does not fit neatly into Django's structure.
- Best for: Small to medium sized applications, APIs, microservices, and developers who love having complete control over their technology stack.
- Tradeoff: That freedom comes with responsibility. You have to make more decisions and piece together your stack, which can lead to more setup time and potential "decision fatigue."
FastAPI: The Modern Speedster
FastAPI is the new kid on the block, and it arrived with a bang. Built on modern Python features like type hints and asynchronous programming, its primary focus is on pure performance and an amazing developer experience. As its name suggests, it is incredibly fast, often rivaling the performance of applications written in Go or NodeJS.
Its killer feature is the automatic, interactive API documentation. Just by using standard Python type hints in your code, FastAPI generates beautiful, interactive docs (using Swagger UI and ReDoc) for your API on the fly. This has been a game changer for me when working on teams; it makes the API self documenting and dead simple for frontend developers to consume.
- Best for: High performance APIs, asynchronous applications (like chat apps or streaming services), and projects where data validation and documentation are critical.
- Tradeoff: It is newer, so the ecosystem of plugins and third party extensions is not as vast as Django's or Flask's. It also leans heavily on modern Python features, which might be a bit of a learning curve for some.
To help you visualize the differences, here is a quick head to head comparison.
Comparing Python Web Frameworks
| Feature | Django | Flask | FastAPI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Batteries Included | Microframework | Performance First |
| Learning Curve | Moderate to High | Low | Low to Moderate |
| Use Case | Full Stack Web Apps | Microservices, APIs | High Performance APIs |
| Async Support | Yes (evolving) | Yes (via extensions) | Native & Core |
| Admin Panel | Built in | Via extensions | Via extensions |
Ultimately, choosing your framework is a personal journey. My advice? Do not get stuck in analysis paralysis for too long.
Pick the one that seems to fit your project's immediate needs, build a small "hello world" app with it, and see how it feels. You will learn far more from writing a few lines of code than you will from reading another dozen articles. Just get started.
Architecting Your Application for Success
You have picked your framework. Awesome. Now what? Before you hammer out a single line of code, we need to talk about the blueprint. This is where we lay the groundwork to prevent a world of pain later on.
I have been there, so excited about a new idea that I just started coding. The result? A tangled mess that was impossible to debug, let alone add new features to. Every change felt like performing surgery on a plate of spaghetti. We are not going to make that mistake here.
This section is our deep dive into structuring your application for the long haul. Getting this architectural phase of your app development with python right will save you countless headaches and make your future self very, very grateful.
Establishing a Clean Foundation
A well organized project structure is like a clean, well lit workshop. You know exactly where every tool is, making it easy to build and fix things. A messy structure is that dark, cluttered garage where you spend half your time just looking for a screwdriver.
Your project's layout should be logical and totally predictable. For most scalable apps, I have found a structure like this works wonders:
config/: This is home base for all your project settings. Think database connections, environment variables, and any framework specific configurations.apps/: This is where the magic happens. Each distinct part of your application gets its own module here. For instance, you might have anaccountsapp for user management and aproductsapp for ecommerce logic.core/: A handy spot for shared utilities, custom middleware, or any base model classes that get used across multiple apps.tests/: No surprises here. All your tests go in this directory, mirroring the structure of yourappsfolder.
This kind of separation makes it immediately obvious where to find code for a specific feature. It is also a massive help for new team members trying to get up to speed.
Managing Dependencies Like a Pro
Python's massive ecosystem of packages is one of its greatest strengths, but it can turn into a nightmare if you are not careful. Ever had that classic "but it works on my machine!" argument? Nine times out of ten, it is due to mismatched package versions.
This is where a modern dependency manager like Poetry becomes your best friend. While pip and a requirements.txt file get the job done, Poetry offers a much more robust and deterministic workflow.
Why I Swear By Poetry: It generates a poetry.lock file that locks down the exact versions of all your dependencies and their sub dependencies. This guarantees that every developer, and your production server, is running the exact same environment, wiping out an entire category of frustrating bugs.Poetry also handles virtual environments and manages your pyproject.toml file, giving you a single, sane tool for all things dependencies.
Designing for Scalability and Sanity
Good architecture really boils down to one thing: separating concerns. This simply means each part of your application has one clear responsibility and does not interfere with other parts. This principle is your guiding light for writing code that does not crumble under its own weight.
A fantastic way to enforce this is by using a service layer. Instead of cramming all your business logic directly into your views or API endpoints, you pull it out into separate service functions or classes.
Here is how the responsibilities break down:
- The View/Controller: Its only job is to handle the HTTP request and response. It takes incoming data, calls the right service, and sends back the result.
- The Service Layer: This is where the core business logic lives. It coordinates data, talks to different models, and performs the actual work.
- The Model/ORM Layer: This layer's sole responsibility is interacting with the database: fetching, creating, updating, and deleting records.
This separation makes your code infinitely easier to test. You can test your business logic in the service layer without having to fake an entire HTTP request. It also makes your API design cleaner; a solid grasp of HTTP methods like PUT vs PATCH is crucial here for building logical and predictable endpoints.
This approach also sets you up for future growth. If your app becomes wildly successful and you need to scale, you are already thinking in terms of services. You can start exploring patterns from the world of microservices. For those curious, our guide on the top microservices architecture best practices offers some great insights that are valuable even if you are building a monolith. Thinking about these concepts early on is what separates a good app from a great one.
From Your Laptop to the Live Web
An app that only runs on your machine is a great start, a fantastic hobby, even. But we are aiming for something bigger. We want a production grade application that serves real users, and that means bridging the gap between your laptop and the live web. This is the moment your project truly comes to life.
This part of the journey, venturing into testing, deployment, and automation, can feel intimidating. But the goal here is not to become a DevOps expert overnight. It is about building a clear, repeatable process for shipping your code with confidence.
Making Peace with Testing
Let us be honest: testing can feel like a chore. For a long time, I treated it as an afterthought, something I would get to "later" when I had more time. Of course, "later" rarely came, and I paid the price with late night bug hunts and stressful deployments.
Everything changed when I found tools like pytest. It completely transformed testing from a tedious task into my most reliable safety net. A good test suite gives you the freedom to refactor and add new features without that constant, nagging worry that you might break something.
Let us write a simple, practical test right now. Imagine we have a utility function that formats a user's full name.
# in your_app/utils.py
def format_full_name(first_name: str, last_name: str) -> str:
"""Combines first and last names into a title cased full name."""
if not first_name or not last_name:
return ""
return f"{first_name.strip().title()} {last_name.strip().title()}"
Now, we will write a pytest test for it. We are not just checking the "happy path"; we are thinking about edge cases, like extra whitespace or empty inputs.
# in tests/test_utils.py
from your_app.utils import format_full_name
def test_format_full_name_standard():
assert format_full_name("kuldeep", "pisda") == "Kuldeep Pisda"
def test_format_full_name_with_whitespace():
assert format_full_name(" kuldeep ", " pisda ") == "Kuldeep Pisda"
def test_format_full_name_empty_inputs():
assert format_full_name("", "pisda") == ""
assert format_full_name("kuldeep", "") == ""
With just those three simple tests, we have created a safety harness. Now, anyone who modifies this function in the future can instantly verify they have not broken existing behavior. This is the bedrock of shipping with confidence.
Demystifying Deployment
Deployment is just the process of taking your code and making it accessible on the internet. In the past, this was a nightmare of managing servers, configuring networks, and a whole lot of system administration headaches.
Thankfully, things are much simpler today with Platform as a Service (PaaS) providers.
PaaS options like Render or Heroku handle almost all of the infrastructure complexity for you. You just connect your GitHub repository, tell them how to run your app, and they take care of the rest. This lets you focus on building features, not managing servers.
Key Takeaway: PaaS is your fastest path to a live application. It abstracts away the complex world of servers, databases, and networking, allowing you to deploy a Python app in minutes, not days.
While PaaS is fantastic for getting started, containerization tools like Docker offer another level of consistency and portability. Docker packages your app and all its dependencies into a standardized "container" that runs identically anywhere. To get up and running with a more robust setup, check out our guide on a Docker setup that feels like a Hollywood blockbuster.
The Magic of CI/CD
Once your app is live, you will want to update it. The manual way, running tests, logging into a server, pulling code, is slow and incredibly error prone. This is where a Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipeline becomes a total game changer.
At its core, a CI/CD pipeline automates your release process. It is a series of steps that automatically fire every time you push code to your repository. A basic pipeline might look like this:
- Push Code: You push a new feature to your GitHub repository.
- Run Tests: A service like GitHub Actions automatically runs your entire
pytestsuite. - Build & Deploy: If all the tests pass, the service builds your app and deploys it to your PaaS provider.
This automation creates a fast, reliable feedback loop. You can ship small changes multiple times a day with confidence, knowing that your automated process is always watching your back. Setting up a basic pipeline with GitHub Actions is surprisingly straightforward and one of the highest leverage skills you can learn.
This solid foundation in testing and automated deployment is not just good practice; it is a highly sought after skill. Python's dominance is clear; by 2025, over 1.19 million job listings on LinkedIn required Python skills, a testament to its broad use in AI, data science, and web development. Mastering these production ready skills makes you incredibly valuable in today's market.
Lessons Learned from the Trenches
Theory is great, but the real world is messy. I cannot count the number of projects where the most important lessons came from a late night bug hunt or a "why did not I think of that?" moment.
This is the stuff you will not find in the official docs, it is the hard won wisdom that comes from watching things break in production.
Think of this section as a collection of my professional scars and the stories behind them. My goal is to help you sidestep some of the common landmines that trip up even seasoned developers building Python apps. These are the practical insights that truly separate a junior dev from a seasoned pro.
The Siren Song of Premature Optimization
One of the biggest traps you can fall into is premature optimization. I once torched a full week optimizing a database query because I was sure it would become a bottleneck. Turns out, that endpoint was barely ever hit. The real performance hog was a completely unrelated background task I had not even considered.
My effort was a total waste. Worse, I added complexity to the codebase to solve a problem that did not even exist. The lesson was painful but crystal clear.
Wait for the Pain: Do not optimize anything until you have data. Use profiling tools to find the actual bottlenecks before you start rewriting perfectly good code. Most of the time, especially early on, the simplest and most readable solution is the right one.
Database Migrations Are Not an Afterthought
Ignoring database migrations is like ignoring a small leak in your roof. It is no big deal at first, but eventually, the whole ceiling comes crashing down.
I have seen teams manually apply SQL changes to production databases, which almost always leads to inconsistent states and catastrophic rollbacks. This is a five alarm fire waiting to happen.
- Make migrations a habit: Run them as a core part of your local development workflow.
- Test your migrations: Make sure they are reversible and do not lock up your tables for an eternity.
- Never, ever run them manually in production: This needs to be a non negotiable step in your automated deployment pipeline.
Treat your database schema with the same respect you give your application code. It is not some separate entity; it is the foundation your entire system is built on.
Logging Is Your Best Detective
When something breaks at 3 AM, good logs are the only thing standing between you and a full blown meltdown. For years, my logging was an afterthought, just a few random print() statements scattered around.
That changed forever after I spent an entire night debugging an issue that would have taken five minutes to solve with one well placed log message. Now, I am a logging fanatic.
Your logs need to tell a story. They should include crucial context like user IDs, request IDs, and any relevant state. Adopting structured logging (using JSON) is a game changer, making your logs searchable and infinitely more powerful when you are under pressure.
Python's growth in the USA is a testament to its professional power, with adoption surging by 7 percentage points between 2024 and 2025. This is driven by AI and data tools in critical fields like finance and healthcare. With average Python developer salaries hitting $120,000 to $150,000, mastering production practices like logging is not just good engineering, it is a vital career skill. You can discover more insights about Python's future in the USA.
Handle Your Secrets Securely
Please, for the love of all that is holy, do not commit API keys, database passwords, or any other secrets directly into your Git repository. I still see this happening, and it is the digital equivalent of leaving your house keys under the doormat with a neon sign pointing to them.
Use environment variables and a tool like python-dotenv for local development. For production, you absolutely should be using your cloud provider's secret management service (like AWS Secrets Manager or Google Secret Manager). It is a simple change that prevents a massive, resume updating security breach.
Common Python App Development Questions
As you get your hands dirty building your app, you are going to have questions. It is just part of the process, every developer hits these walls, myself included. This last section is all about tackling those frequent "what about..." moments I hear from developers building with Python.
Let us clear up some of the most common sticking points so you can keep moving forward.
Can Python Handle High Traffic Applications?
This one comes up a lot, usually driven by the old myth that interpreted languages are just too slow for the big leagues.
The short answer? Absolutely, yes.
Sure, Python itself is not winning any raw speed contests against C or Go. But in a well architected web application, the language's execution speed is rarely the actual bottleneck. Modern frameworks like FastAPI are built from the ground up for performance, using async programming to juggle thousands of concurrent connections without breaking a sweat.
The real performance gains come from smart database queries, effective caching, and a solid infrastructure. Instagram, Spotify, and Netflix rely on Python for huge parts of their backend, proving it can scale to absolutely massive user loads.
Is Python Good For Frontend Development?
Straight up: Python's kingdom is the backend. It is a beast at running your server, talking to the database, handling business logic, and serving up APIs.
For the frontend, the part your users actually see and click on, you will almost always be using a dedicated JavaScript framework. Think React, Vue, or Svelte.
This is not a limitation; it is just good, modern web architecture. The two sides have a clean separation: Python provides the data, and JavaScript builds the user interface that consumes it.
How Should I Manage Project Dependencies?
Getting your dependencies right is not just a nice to have; it is non negotiable for a sane development process. The first step, always, is to use a virtual environment.
Think of a virtual environment as an isolated sandbox just for your project. It makes sure that the specific library versions your app depends on (like Django==4.2 or SQLAlchemy==1.4) do not clash with other projects on your machine. Python's built in venv module is a perfect place to start.
When you are ready for more firepower, tools like Poetry or Pipenv are fantastic. They create a lockfile (poetry.lock or Pipfile.lock) that guarantees every single developer on your team, and your production server, is running the exact same set of dependencies. This simple practice kills off an entire class of "but it works on my machine!" bugs before they even start.
Ready to build a robust, scalable Python application but need expert guidance to accelerate your roadmap? Kuldeep Pisda specializes in helping startups strengthen their technical foundations with thoughtful architecture and pragmatic delivery. Let's build something great together.
Subscribe to our newsletter.
Become a subscriber receive the latest updates in your inbox.



Member discussion